The language B curriculum should allow students to explore a variety of languages, contexts, and other intercultural subtleties. When designing the language B course, the first thing to consider is striking a balance in the course design to make these student explorations possible. Get a head start with this resource!

In this section, you will deep-dive into everything you need to consider when designing an intentional, student-centered language B course. Let’s get started!
Underpinning elements
Before you start building your outline, it is important to understand the five underpinning elements of the language B course.
The first element is prescribed themes which students should explore through a well-curated selection of authentic oral and written text types.
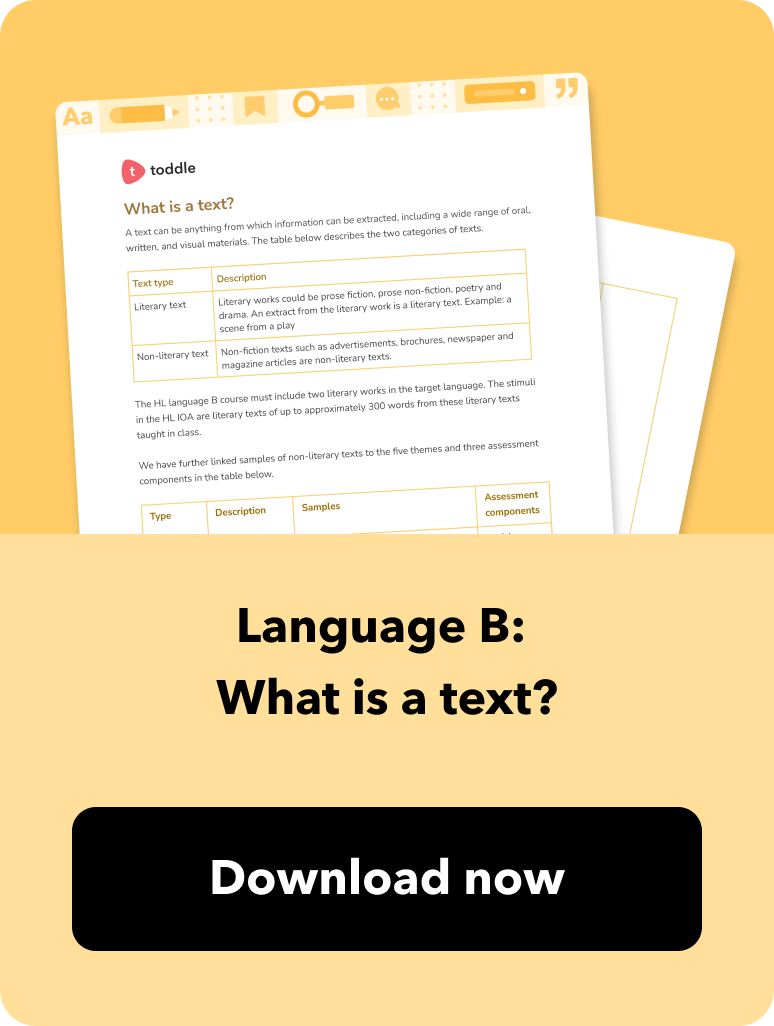 Throughout the course, students engage with these texts and create their own for different audiences, contexts, and purposes while developing important receptive, productive, and interactive skills. Your goal is to select texts that help students understand how language works in a particular context and strengthen their conceptual understanding. Ultimately, your intention, when designing the course, is to infuse an appreciation of different cultures and promote international mindedness.
Throughout the course, students engage with these texts and create their own for different audiences, contexts, and purposes while developing important receptive, productive, and interactive skills. Your goal is to select texts that help students understand how language works in a particular context and strengthen their conceptual understanding. Ultimately, your intention, when designing the course, is to infuse an appreciation of different cultures and promote international mindedness.
Let us now dive into the prescribed themes in more detail.
Exploring language B themes
The language B course is designed around the five prescribed themes which must be addressed equally in the two-year course. For each theme, you are required to select appropriate text types that help situate classroom learning in real-world contexts. Each prescribed theme comes with a range of recommended subtopics and questions to support classroom explorations and prompt text selection. These are outlined below:
Download this graphic as a poster to display in your classrooms or keep it handy while you design your course!
In addition to fostering students’ linguistic abilities and skills, a course designed around these themes also creates opportunities for students to communicate about matters of personal and global significance.
Principles of course design
When you plan a course outline, all parts of the language B curriculum should complement each other and be integrated with the objective of developing students’ abilities to communicate effectively in the target language. Considering the three principles of language B course design – variety, transparency, and integration – will help you achieve this. As you work towards designing your course, here are some implementation ideas for each principle:


Get your hands on this sample course outline and brainstorming template for language B! Weave together all the course elements and design principles, and jump straight to creating your own language B course!




